- Screwless push-in type connection for simple and easy connection
- Compact, space-saving design
- Ideal for PLCs and motion device I/O
- DIN rail mount and screw mount installation
※ Autonics CH/CO series I/O terminal block cables are recommended for best performance.
Screwless Push-In Connection

Slim type

Operation Indicator

Screw Mount

DIN Rail Mount
Model
| Type | The Number of Terminals Points | The Number of Connector Pins | Connector (Controller) | Mounting Method | Operation Indicator | Input Logic | Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Screwless | 20-Point | 20-Pin | XG4A-2031 | DIN Rail/ Screw Mount |
– | – | AFL-H20 |
| 16-Point*¹ | Y | NPN | AFL-H20-LN | ||||
| Y | PNP | AFL-H20-LP | |||||
| 26-Point | 26-Pin | XG4A-2631 | – | – | AFL-H26 | ||
| 40-Point | 40-Pin | HIF3BA-40PA-2.54DSA | AFL-H40 | ||||
| 32-Point*² | Y | NPN | AFL-H40-LN | ||||
| Y | PNP | AFL-H40-LP | |||||
| 50-Point | 50-Pin | HIF3BA-50PA-2.54DSA | – | – | AFL-H50 | ||
| HIF3BB-50PA-2.54DSA | AFL-H50B |
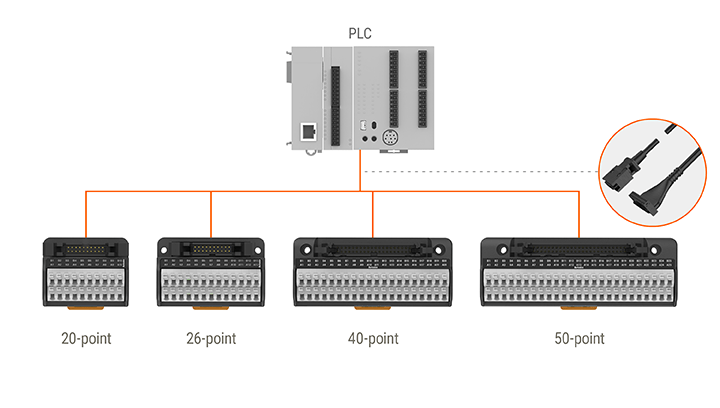
Various Lineup for Flexible Application
The AFL series allows the flexibility for user’s needs and applications with various lineup.
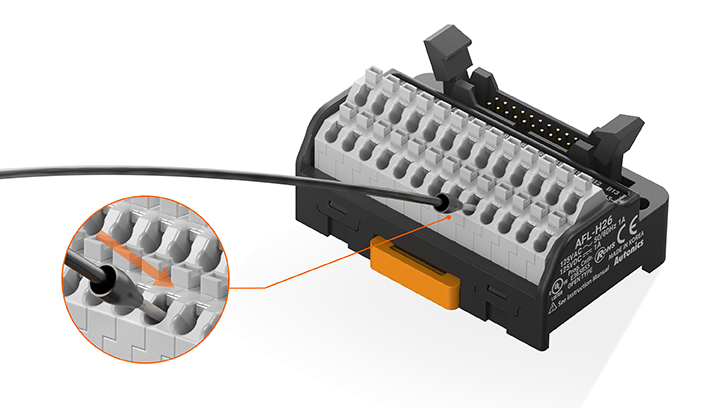
Easy Wiring and Stable Connection with Screwless Push-in Connection
The AFL series feature simple screwless push-in type connection providing easy wiring, secure & durable connection, high vibration resistance, reduced installation time, even tightening.
Flexible Mounting Methods
The AFL series supports both DIN rail mount and screw mount methods, for application in diverse environments.
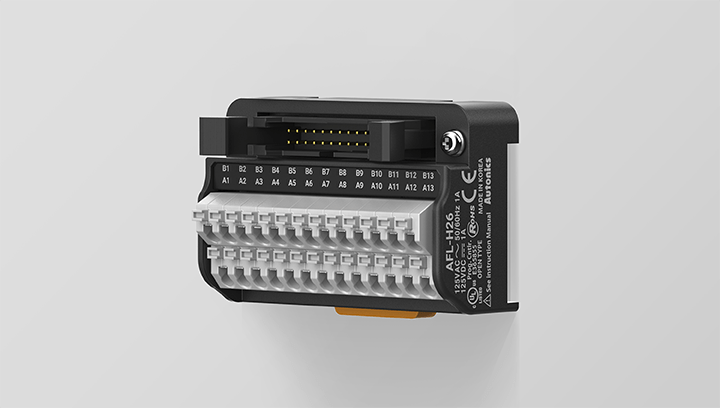


Space-saving Design with Slim Size
The AFL series feature space-saving design with 5 mm terminal pitch for connecting more devices in limited space.

Operation Status Indicators
Users can easily check the status of the terminals with the power indicator (red LED) and operation indicators (blue LED)
* Only on AFL-H20/40-LN(P) models



